Social Interaction Trainer
Effective Communication Skills
Networking and Relationship Building
Confidence Building
Public Speaking Mastery
Emotional Intelligence Development
Assertiveness Training
Conflict Resolution Techniques
Cross-Cultural Communication
Online Etiquette and Digital Communication
Social Skills for Specific Situations
Building Rapport and Influence
Mindfulness and Social Presence

Effective Communication Skills
Introduction to Effective Communication Skills
- Importance of effective communication in personal and professional life
- Overview of what effective communication entails
Verbal Communication
- Tips for clear and concise verbal communication
- Active listening techniques
- The importance of tone, pitch, and pacing
- Strategies for effective public speaking
Nonverbal Communication
- Understanding body language cues
- Using facial expressions and gestures effectively
- Posture and eye contact in communication
- Interpreting nonverbal signals from others
Assertive Communication
- Definition and characteristics of assertive communication
- Techniques for expressing needs and opinions assertively
- Setting boundaries and saying no respectfully
- Handling criticism and feedback assertively
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
- Importance of empathy in communication
- Developing emotional intelligence skills
- Empathetic listening and validating others’ emotions
- Managing emotions during difficult conversations
Conflict Resolution
- Understanding the sources of conflict
- Strategies for resolving conflicts constructively
- Active listening and perspective-taking in conflict resolution
- Negotiation and compromise techniques
Communication in Relationships
- Building trust and rapport in relationships
- Effective communication in romantic relationships, friendships, and family dynamics
- Conflict resolution and healthy communication habits in relationships
Cultural Competence
- Understanding cultural differences in communication styles
- Respecting cultural norms and customs in communication
- Building cross-cultural communication skills
Professional Communication
- Writing effective emails and business correspondence
- Communicating professionally in the workplace
- Presentation skills and effective meeting communication
- Networking and building professional relationships
Practical Exercises and Activities
- Role-playing scenarios for practicing communication skills
- Reflective exercises to assess communication strengths and areas for improvement
- Group discussions and activities to promote effective communication in various contexts
Additional Resources and Further Reading
- Recommended books, articles, and websites on effective communication skills
- Links to online courses and workshops for further skill development

Networking and Relationship Building
Introduction to Networking and Relationship Building
- Importance of networking and building relationships in personal and professional life
- Overview of what networking entails and its benefits
Building a Networking Mindset
- Developing a positive attitude towards networking
- Overcoming common networking fears and barriers
- Recognizing the value of networking for personal and career growth
Networking Strategies
- Identifying networking opportunities both online and offline
- Setting networking goals and objectives
- Techniques for effective networking conversations and interactions
- Leveraging social media platforms for networking
Creating a Professional Network
- Building and nurturing professional relationships
- Networking with colleagues, mentors, and industry peers
- Strategies for expanding your professional network
- Maintaining relationships over time and staying connected
Networking Events and Activities
- Tips for networking at conferences, seminars, and industry events
- Approaching and initiating conversations with new contacts
- Following up with contacts after networking events
- Maximizing the value of networking opportunities
Online Networking
- Utilizing professional networking platforms such as LinkedIn
- Building an engaging and professional online presence
- Networking etiquette in online forums and communities
- Leveraging online tools for networking and relationship building
Networking for Career Development
- Using networking to explore career opportunities and advance professionally
- Seeking mentorship and guidance from within your network
- Networking strategies for job search and career transitions
- Building a personal brand through networking
Relationship Building Skills
- Cultivating trust and rapport in relationships
- Active listening and empathy in relationship building
- Building mutually beneficial relationships
- Resolving conflicts and managing disagreements in relationships
Networking for Entrepreneurs and Business Owners
- Building a network of clients, partners, and collaborators
- Networking strategies for growing a business or startup
- Leveraging networking for business development and sales
Maintaining and Strengthening Relationships
- Strategies for staying connected with your network
- Nurturing relationships through regular communication and support
- Showing appreciation and gratitude to your network contacts
- Reconnecting with dormant contacts and revitalizing relationships
Practical Exercises and Activities
- Networking role-play scenarios and practice sessions
- Networking challenges and goal-setting exercises
- Group discussions and networking workshops
Additional Resources and Further Reading
- Recommended books, articles, and podcasts on networking and relationship building
- Links to online courses and workshops for further skill development

Confidence Building
Understanding Confidence
- Definition of confidence and its importance in personal and professional life
- Differentiating between self-confidence and self-esteem
- Recognizing the impact of confidence on various aspects of life
Identifying Barriers to Confidence
- Common barriers to confidence, such as self-doubt, fear of failure, and negative self-talk
- Exploring the root causes of low confidence
- Recognizing the role of past experiences and beliefs in shaping confidence levels
Building Self-Awareness
- Techniques for developing self-awareness and understanding one’s strengths and weaknesses
- Identifying and challenging limiting beliefs and negative thought patterns
- Cultivating a growth mindset and embracing opportunities for learning and growth
Setting Realistic Goals
- Setting achievable goals to boost confidence and motivation
- Breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks
- Celebrating progress and accomplishments along the way
Developing Positive Self-Talk
- Practicing positive affirmations and self-encouragement
- Reframing negative thoughts and beliefs into more empowering perspectives
- Using visualization and mental imagery to reinforce confidence
Stepping Out of Comfort Zones
- Understanding the role of discomfort in personal growth and confidence building
- Encouraging taking calculated risks and trying new experiences
- Embracing failures and setbacks as opportunities for learning and resilience
Building Competence and Skills
- Investing in personal and professional development to build competence and expertise
- Setting aside time for skill-building activities and continuous learning
- Recognizing and celebrating achievements and progress in skill development
Cultivating Supportive Relationships
- Surrounding oneself with positive and supportive individuals
- Seeking encouragement and feedback from trusted mentors, friends, and family members
- Establishing boundaries and distancing oneself from negative influences
Practicing Self-Care
- Prioritizing self-care activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being
- Setting boundaries and managing stress to prevent burnout
- Incorporating relaxation techniques and mindfulness practices into daily routines
Taking Action and Building Momentum
- Encouraging taking small, consistent steps towards goals
- Overcoming procrastination and perfectionism through action
- Celebrating achievements and reinforcing confidence through positive reinforcement
Embracing Imperfection and Self-Acceptance
- Embracing imperfections and recognizing that nobody is perfect
- Cultivating self-compassion and practicing forgiveness towards oneself
- Fostering a sense of self-acceptance and unconditional self-worth
Additional Resources and Further Reading
- Recommended books, articles, and resources on confidence building
- Links to online courses and workshops for further skill development
Introduction to Public Speaking
- Importance of public speaking skills in personal and professional life
- Overview of what public speaking mastery entails
Overcoming Public Speaking Anxiety
- Understanding the root causes of public speaking anxiety
- Techniques for managing anxiety and nervousness
- Building confidence and self-assurance as a speaker
Preparing for a Speech
- Researching and understanding the audience and occasion
- Structuring a speech for maximum impact (introduction, body, conclusion)
- Crafting compelling openings and closings
Effective Delivery Techniques
- Utilizing vocal variety (tone, pitch, pace, volume) for emphasis and engagement
- Using body language effectively (gestures, posture, eye contact)
- Practicing articulation and enunciation for clarity
Engaging the Audience
- Techniques for capturing and maintaining audience attention
- Incorporating storytelling, anecdotes, and humor into speeches
- Encouraging audience interaction and participation
Mastering Visual Aids
- Designing visually appealing and effective slides or visual aids
- Using slides to enhance, rather than distract from, the speech
- Tips for managing technical issues during presentations
Handling Q&A Sessions
- Strategies for responding confidently to audience questions
- Techniques for handling challenging or unexpected questions
- Ensuring clarity and understanding in responses
Practicing and Rehearsing
- Importance of practice and rehearsal in mastering public speaking
- Techniques for effective practice sessions (e.g., recording, peer feedback)
- Overcoming common rehearsal pitfalls (e.g., over-rehearsing, under-rehearsing)
Dealing with Speaking Challenges
- Strategies for overcoming speech impediments or pronunciation issues
- Tips for managing stage fright or performance anxiety during speeches
- Techniques for maintaining composure and professionalism in difficult speaking situations
Continuous Improvement
- Seeking feedback and constructive criticism for ongoing improvement
- Setting goals for continued growth and development as a speaker
- Incorporating lessons learned from each speaking experience into future presentations
Building Confidence Beyond the Stage
- Applying public speaking skills to everyday communication situations
- Leveraging speaking opportunities for personal and professional growth
- Recognizing the broader impact of effective communication skills in various aspects of life
Additional Resources and Further Reading
- Recommended books, articles, and resources on public speaking mastery
- Links to online courses, workshops, and public speaking clubs for further skill development

Emotional Intelligence Development
Self-awareness: Start by becoming more aware of your own emotions. Pay attention to how you feel in different situations and reflect on why you feel that way. Journaling can be a helpful tool for increasing self-awareness.
Self-regulation: Once you’re aware of your emotions, work on regulating them. Practice techniques like deep breathing, mindfulness, or taking a break when you’re feeling overwhelmed. This can help you respond to situations in a more constructive way.
Empathy: Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. Practice putting yourself in someone else’s shoes and seeing things from their perspective. Listen actively and validate their emotions without judgment.
Social skills: Build strong relationships by developing your communication and interpersonal skills. Practice active listening, assertiveness, and conflict resolution. Work on building rapport and connecting with others on an emotional level.
Emotional awareness in others: Pay attention to the emotions of those around you. Notice nonverbal cues like body language and facial expressions, and use them to gauge how others are feeling. This can help you respond appropriately and effectively in social situations.
Continuous learning: Emotional intelligence is a skill that can be developed over time. Keep learning and growing by seeking feedback from others, reading books and articles on emotional intelligence, and attending workshops or training sessions.
Practice self-care: Take care of your physical and mental well-being, as they are closely linked to emotional intelligence. Get enough sleep, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and make time for activities that you enjoy. Prioritize activities that help you recharge and reduce stress.
Reflect and review: Regularly reflect on your emotions, reactions, and interactions with others. Consider what went well and what you could improve upon. Use this feedback to adjust your behavior and continue growing in your emotional intelligence journey.
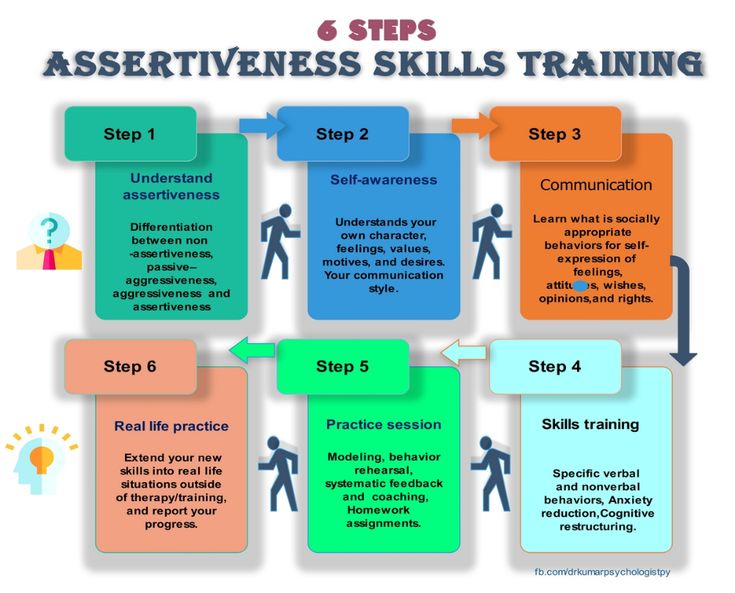
Assertiveness Training
Understanding assertiveness: Participants learn about the differences between passive, aggressive, and assertive behavior. They explore the benefits of assertiveness, such as improved communication, increased self-confidence, and better relationships.
Identifying personal rights: Assertiveness training often involves identifying and understanding one’s own rights and boundaries. This includes the right to express opinions and feelings, the right to say no, and the right to ask for what one needs.
Communication skills: Participants learn effective communication skills, such as active listening, using “I” statements to express thoughts and feelings, and giving and receiving feedback constructively.
Setting boundaries: Assertiveness training helps individuals learn how to set and maintain boundaries in various situations, such as at work, in relationships, and with family and friends. This involves clearly communicating limits and consequences to others.
Assertive behavior rehearsal: Participants practice assertive communication and behavior through role-playing exercises and real-life scenarios. This allows them to develop confidence and become more comfortable expressing themselves assertively.
Managing emotions: Assertiveness training often includes techniques for managing emotions, such as relaxation exercises, deep breathing, and mindfulness practices. This helps individuals stay calm and composed when expressing themselves assertively.
Dealing with criticism and conflict: Participants learn how to handle criticism and conflict assertively, without becoming defensive or aggressive. They practice techniques for giving and receiving criticism in a constructive manner and resolving conflicts peacefully.
Building self-confidence: Assertiveness training aims to boost self-esteem and self-confidence by helping individuals recognize their own worth and value, assert their rights, and advocate for themselves effectively.
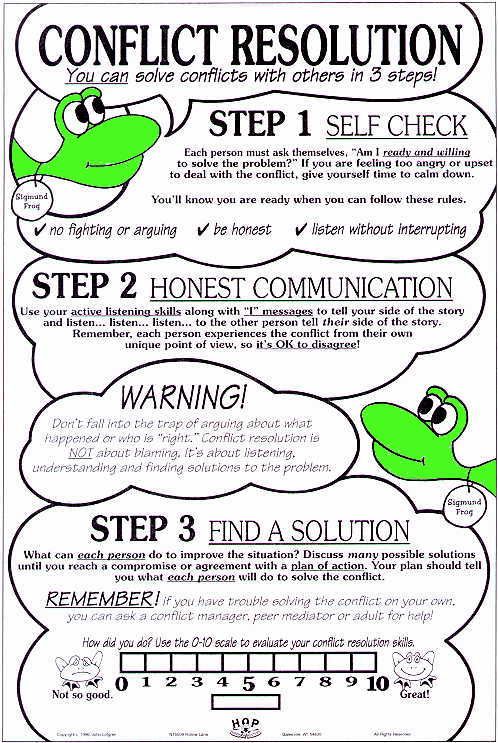
Conflict Resolution Techniques
Active Listening: Encourage all parties involved to actively listen to each other without interrupting. This involves paying full attention to the speaker, paraphrasing what they’ve said to ensure understanding, and asking clarifying questions.
Open Communication: Create a safe and open environment where all parties feel comfortable expressing their thoughts, feelings, and perspectives without fear of judgment or retaliation.
Empathy: Encourage empathy by helping each party understand the other’s perspective, feelings, and needs. This can help foster understanding and mutual respect.
Finding Common Ground: Identify areas of agreement or shared interests between the parties involved. Focus on these commonalities as a starting point for finding a resolution.
Brainstorming Solutions: Encourage creative brainstorming to generate multiple potential solutions to the conflict. Avoid criticizing ideas during this stage and aim for quantity over quality.
Negotiation: Facilitate negotiation between the parties to reach a mutually acceptable solution. Encourage compromise and flexibility while ensuring that all parties’ interests and needs are considered.
Seeking Mediation: If necessary, involve a neutral third party, such as a mediator or arbitrator, to facilitate communication, assist in problem-solving, and help the parties reach a resolution.
Conflict De-escalation: Use techniques to de-escalate tensions and emotions during the conflict resolution process. This may include taking breaks, using humor, or employing relaxation techniques.
Problem-Solving: Encourage a focus on problem-solving rather than blame or fault-finding. Identify the underlying issues contributing to the conflict and work collaboratively to address them.
Setting Ground Rules: Establish ground rules for respectful communication and behavior during the conflict resolution process. This may include guidelines for listening, speaking, and problem-solving.
Time-Outs: If emotions escalate or communication breaks down, suggest taking a temporary break to cool off and collect thoughts before resuming the discussion.
Follow-Up: Once a resolution is reached, follow up with all parties to ensure that the agreement is being implemented and to address any remaining concerns or issues.

Cross-Cultural Communication
Cultural Awareness: Develop an understanding of your own cultural values, beliefs, and communication styles, as well as those of other cultures. Recognize that cultural differences exist and can influence communication.
Respect and Open-mindedness: Approach cross-cultural interactions with respect, openness, and a willingness to learn from others. Avoid making assumptions or judgments based on stereotypes.
Active Listening: Practice active listening by paying full attention to the speaker, seeking to understand their perspective, and acknowledging their feelings and concerns. Avoid interrupting or rushing to conclusions.
Nonverbal Communication: Be aware of nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, gestures, and eye contact, which can vary significantly across cultures. Avoid misinterpreting nonverbal signals and consider their cultural context.
Clarity and Simplicity: Use clear and simple language, avoiding jargon, slang, or complex vocabulary that may be difficult for non-native speakers to understand. Speak slowly and enunciate clearly, if necessary.
Adaptability: Be flexible and adaptable in your communication style to accommodate cultural differences. Modify your approach based on the cultural norms, expectations, and preferences of the other party.
Ask Questions: Seek clarification if you are unsure about something or if you need more information. Asking questions demonstrates interest and curiosity while helping to avoid misunderstandings.
Avoid Cultural Assumptions: Avoid assuming that all members of a particular cultural group think or behave the same way. Recognize the diversity within cultures and treat each individual as unique.
Feedback and Confirmation: Seek feedback from the other party to ensure mutual understanding and agreement. Confirm that your message has been accurately received and interpreted.
Patience and Tolerance: Be patient and tolerant when communicating across cultures, especially when language barriers or cultural differences present challenges. Avoid becoming frustrated or impatient.
Cultural Sensitivity: Be sensitive to cultural differences in topics such as gender roles, religion, hierarchy, and social customs. Respect cultural norms and avoid behaviors or language that may be offensive or disrespectful.
Continuous Learning: Continuously seek to expand your knowledge and understanding of different cultures through education, exposure, and experience. Cultivate a mindset of lifelong learning and cultural curiosity.

Online Etiquette and Digital Communication
Respect Others: Treat others with respect and courtesy in all online interactions. Avoid offensive language, personal attacks, or hostile behavior. Remember that there are real people behind online profiles.
Be Clear and Concise: Communicate clearly and concisely to ensure that your message is understood. Use proper grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Avoid excessive use of acronyms or emojis, which can be confusing or unprofessional.
Use Proper Tone: Be mindful of your tone when communicating online. Tone can be easily misinterpreted in text-based communication. Strive to convey your message in a friendly and professional tone, and avoid sarcasm or humor that may be misunderstood.
Think Before You Post: Take a moment to think before posting or sending messages online. Consider the potential impact of your words and how they may be perceived by others. Avoid posting impulsively or in anger.
Respect Privacy: Respect the privacy of others by refraining from sharing personal information or private conversations without permission. Be cautious about sharing sensitive information online and use privacy settings to control who can access your content.
Be Responsive: Respond promptly to messages and inquiries to demonstrate respect for others’ time and attention. If you need more time to respond, acknowledge the message and provide an estimated timeframe for your reply.
Use Descriptive Subject Lines: When sending emails or posting in online forums, use descriptive subject lines that accurately summarize the content of your message. This helps recipients quickly understand the purpose of your communication and prioritize their responses.
Stay On Topic: Keep online discussions focused on the relevant topic or subject matter. Avoid derailing conversations with unrelated or off-topic comments. If you want to discuss a different topic, start a new thread or conversation.
Respect Copyright: Avoid plagiarism and respect copyright laws when sharing content online. Give credit to the original creators of content, and obtain permission before using or reposting copyrighted material.
Be Professional: Maintain a professional demeanor in all online interactions, especially in professional or work-related contexts. Avoid engaging in gossip, inappropriate jokes, or unprofessional behavior that may reflect poorly on you or your organization.
Practice Empathy: Consider the perspectives and feelings of others when communicating online. Be empathetic and supportive, especially in sensitive or difficult discussions. Avoid making assumptions about others’ experiences or feelings.
Be Mindful of Timing: Be mindful of time zones and cultural differences when communicating with people from around the world. Avoid sending messages or making posts at inappropriate times that may inconvenience or disturb others.
Social Skills for Specific Situations
Networking Events: Effective social skills are essential for making connections and building professional relationships at networking events. This includes approaches such as initiating conversations, active listening, asking questions, and exchanging contact information.
Job Interviews: Social skills play a significant role in job interviews, as they influence how candidates are perceived by potential employers. Skills such as confidence, communication, active listening, and the ability to articulate ideas clearly can help candidates make a positive impression and effectively convey their qualifications and experiences.
Public Speaking: Public speaking requires strong social skills to engage and connect with the audience. This includes skills such as clear communication, confidence, effective body language, and the ability to tailor the message to the audience’s needs and interests.
Conflict Resolution: Social skills are essential for resolving conflicts and managing disagreements in various settings, including the workplace, relationships, and social groups. Skills such as active listening, empathy, negotiation, and problem-solving can help individuals navigate conflicts constructively and find mutually acceptable solutions.
Teamwork and Collaboration: Effective teamwork relies on strong social skills such as communication, cooperation, trust-building, and conflict resolution. Individuals who possess these skills can collaborate effectively with others, contribute to team goals, and build positive working relationships.
Customer Service: In roles that involve customer service or client interactions, social skills are crucial for building rapport, addressing customer needs and concerns, and delivering excellent service. This includes skills such as empathy, active listening, problem-solving, and effective communication.
Dating and Relationships: Social skills play a significant role in dating and forming romantic relationships. Skills such as communication, empathy, active listening, emotional intelligence, and conflict resolution can help individuals navigate the complexities of dating, build strong connections, and maintain healthy relationships.
Networking Online: In today’s digital age, social skills are also important for networking and building relationships online. This includes skills such as crafting engaging messages, connecting with others on social media platforms, participating in online communities, and maintaining professional etiquette in digital communication.
Negotiation and Persuasion: Social skills are crucial for negotiation and persuasion in various contexts, such as business negotiations, sales interactions, and personal situations. Skills such as effective communication, active listening, empathy, and the ability to understand others’ perspectives can help individuals negotiate favorable outcomes and persuade others to take action or adopt a particular viewpoint.
Social Gatherings and Events: Strong social skills are essential for navigating social gatherings and events, such as parties, weddings, and social outings. This includes skills such as making introductions, engaging in small talk, demonstrating interest in others, and knowing when and how to exit conversations gracefully.


Building Rapport and Influence
Establish Common Ground: Find shared interests, experiences, or values that you have in common with the person you want to connect with. Building on common ground helps create a sense of camaraderie and understanding.
Active Listening: Demonstrate genuine interest in the other person by actively listening to what they have to say. Maintain eye contact, nod occasionally, and ask clarifying questions to show that you are engaged and interested in their perspective.
Empathy: Show empathy by understanding and acknowledging the other person’s feelings, thoughts, and concerns. Empathizing with others helps build trust and strengthens the connection between you.
Authenticity: Be genuine and authentic in your interactions. People are more likely to trust and respect someone who is true to themselves and not trying to be someone they’re not.
Positive Body Language: Pay attention to your body language, as it can significantly impact how others perceive you. Use open and welcoming body language, such as smiling, maintaining good posture, and offering a firm handshake.
Build Trust: Trust is the foundation of rapport and influence. Be reliable, honest, and consistent in your actions and communication. Follow through on your commitments and demonstrate integrity at all times.
Be a Good Communicator: Communicate clearly and effectively, both verbally and nonverbally. Tailor your communication style to match the preferences of the person you’re interacting with, and ensure that your message is understood.
Find Opportunities to Connect: Look for opportunities to connect with others outside of formal settings. This could include networking events, social gatherings, or informal meetings. Building rapport in a relaxed and casual environment can be highly effective.
Be Respectful: Treat others with respect and courtesy, regardless of their position or background. Show appreciation for their ideas and contributions, and avoid criticizing or belittling them.
Offer Value: Look for ways to add value to the relationship by offering support, assistance, or valuable insights. Be generous with your time and resources, and be willing to help others achieve their goals.
Follow Up: Maintain regular communication and follow up with people you’ve connected with to strengthen the relationship over time. This could include sending a quick email to check in, sharing relevant articles or resources, or inviting them to future events or opportunities.
Lead by Example: Demonstrate leadership qualities such as integrity, competence, and humility. Lead by example and inspire others through your actions and behavior.

Mindfulness and Social Presence
Mindfulness in Social Interactions: Mindfulness involves being fully present and engaged in the current moment, without judgment or distraction. When applied to social interactions, mindfulness helps you focus your attention on the person you’re interacting with, listening attentively to what they’re saying, and responding thoughtfully. This can lead to more meaningful and authentic connections with others.
Awareness of Social Cues: Mindfulness can enhance your awareness of social cues, such as body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions. By being mindful of these cues, you can better understand the emotions and intentions of others, allowing for more empathetic and effective communication.
Reduced Social Anxiety: Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, can help reduce social anxiety and nervousness in social situations. By grounding yourself in the present moment and calming your mind, you can approach social interactions with greater ease and confidence.
Enhanced Social Presence: Social presence refers to the sense of being “present” and engaged in social interactions, both online and offline. Mindfulness can enhance your social presence by helping you cultivate a genuine and authentic connection with others. When you’re mindful, you’re more likely to communicate clearly, express empathy, and project confidence, which can contribute to a stronger social presence.
Improved Communication Skills: Mindfulness can improve your communication skills by encouraging active listening, empathy, and nonjudgmental communication. By being fully present in the conversation and attuned to the other person’s needs and emotions, you can respond more effectively and build rapport more easily.
Mindful Speech: Mindfulness can also help you become more mindful of your own speech and communication style. By pausing to consider your words before speaking and speaking with intention and clarity, you can avoid misunderstandings and communicate more effectively with others.
Cultivating Empathy: Mindfulness practices often involve cultivating empathy and compassion towards oneself and others. By developing a greater sense of empathy, you can better understand and connect with the experiences and perspectives of those around you, leading to deeper and more meaningful relationships.
Managing Distractions: In today’s digital age, it’s easy to become distracted during social interactions by smartphones, notifications, and other distractions. Mindfulness can help you manage these distractions by bringing your attention back to the present moment and the person you’re interacting with, allowing for more focused and meaningful communication.
Overview: The Social Interaction Trainer is responsible for designing and implementing training programs aimed at improving individuals’ social skills, communication abilities, and interpersonal relationships. This role involves creating structured learning modules, conducting interactive workshops, and providing one-on-one coaching to help clients develop confidence and effectiveness in various social situations.





Recent Comments